Infectious diseases can spread quickly in schools and other educational institutions due to close contact, sharing surfaces, and common spaces. Here is the basic information about the most common infectious diseases spreading among children in schools, their prevention methods, and consequences.
1. Respiratory tract infections
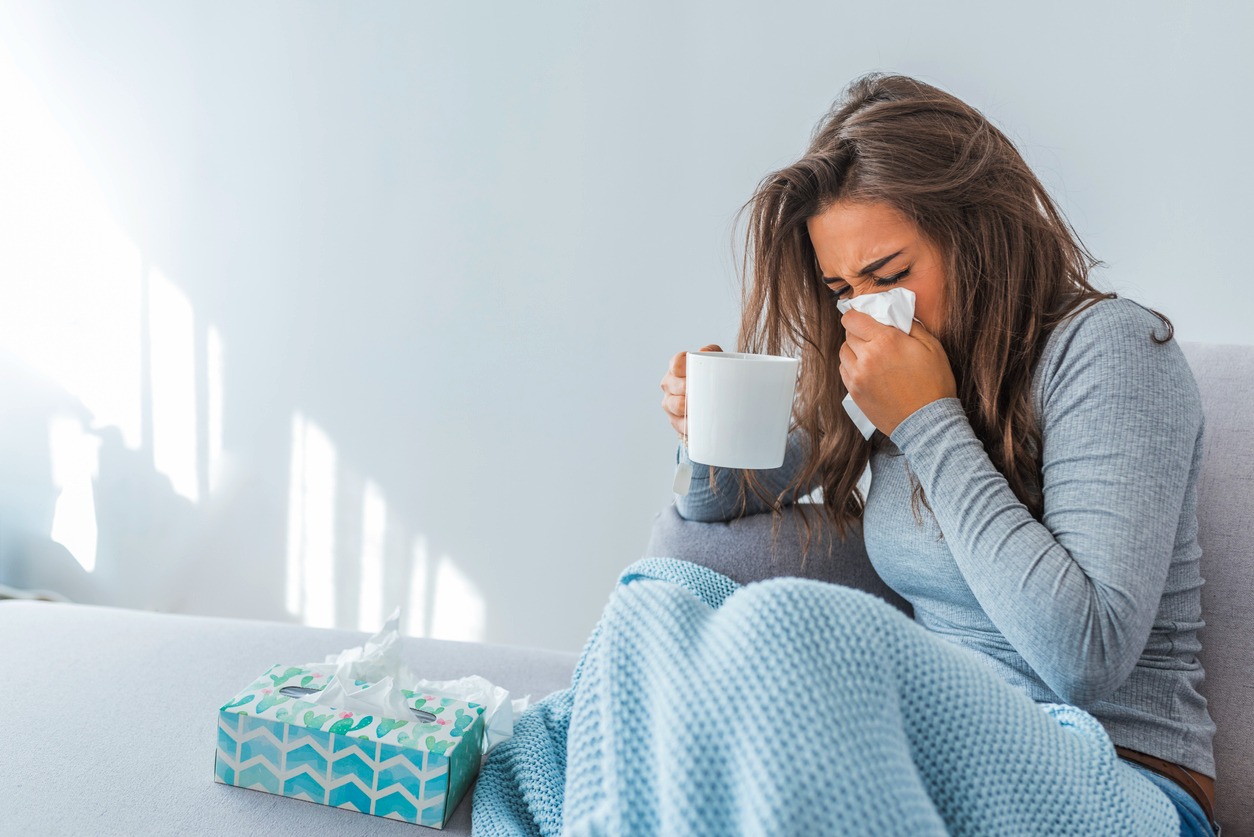
- Influenza: Influenza spreads through respiratory droplets and can cause significant absenteeism among children and teachers at school.
- Common cold: The common cold is caused by various viruses (e.g., rhinoviruses) that easily spread among children through coughing, sneezing, or sharing toys and surfaces.
- COVID-19: Although younger children often experience milder symptoms, COVID-19 still spreads easily in schools, especially due to new virus variants that can evade immunity from vaccines or previous infections.
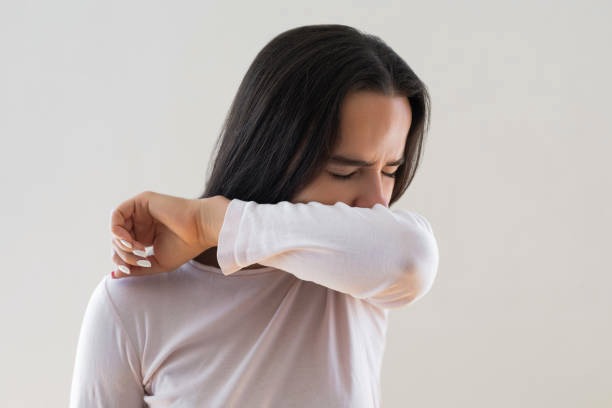
- Prevention: Encouraging regular hand washing, covering the nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing, ensuring good ventilation – all these help reduce the spread of respiratory infections. Vaccination programs (e.g., for influenza and COVID-19) are also important.
2. Gastrointestinal infections
- Norovirus: This highly contagious virus causes vomiting and diarrhea, and tiny traces on surfaces can infect others.
- Rotavirus: Primarily affects infants and young children and spreads through contaminated hands, surfaces, and food. Causes severe diarrhea and vomiting.
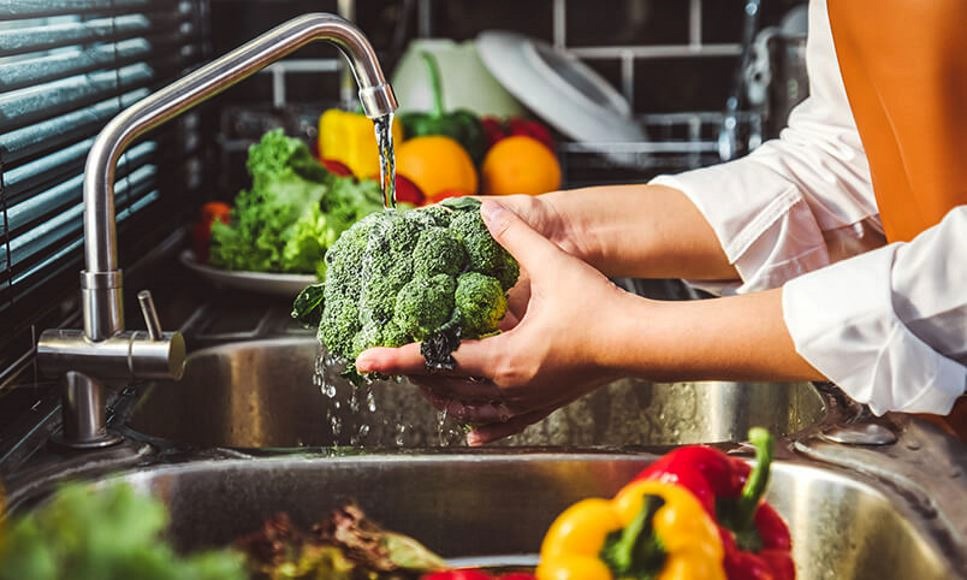
- E. coli and Salmonella: These bacterial infections cause gastrointestinal disturbances and often spread through contaminated food or unwashed hands.
- Prevention: Thorough hand hygiene, especially before eating and after using the toilet, is essential. Regular cleaning of frequently touched surfaces and adherence to food safety rules are also important.
3. Vaccine-preventable diseases
- Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR): These diseases spread easily in schools, especially in communities with low vaccination coverage.
- Whooping cough: A highly contagious disease causing severe coughing and dangerous for young children.
- Chickenpox: Although rarer due to vaccines, outbreaks still occur among unvaccinated children.
- Prevention: Ensuring children receive recommended vaccines is the most effective way to protect against these diseases. Schools often require proof of vaccination.
4. Skin and parasite-caused infections
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD): Caused by enteroviruses, mostly affects young children and spreads through saliva, mucus, and surfaces.
Impetigo: A bacterial skin infection spreading through direct contact with infected skin or surfaces.
Lice and scabies: Although not diseases, they can spread quickly through direct head contact or sharing items like hats or brushes.
Prevention: Regular disinfection of surfaces, avoiding sharing personal items, and teaching hygiene rules to children can reduce the spread of these infections.
5. Streptococcal infections
- Streptococcal sore throat: Spreads through respiratory droplets, common among school-age children, and can cause complications if untreated.
- Scarlet fever: Caused by the same bacteria as streptococcal sore throat, this infection can cause a red, rough rash and often requires antibiotics.
- Prevention: Early diagnosis and treatment, as well as strengthening hand hygiene, help limit outbreaks of these infections.
Impact on schools and educational institutions
Outbreaks of infectious diseases in schools can cause:
- High absenteeism: This affects both students and teachers and disrupts the learning process and school activities.
- Possible closures: Large-scale outbreaks, especially of highly contagious diseases, can force temporary school closures.
- Increased healthcare costs and stress: Managing outbreaks requires resources for infection control and healthcare.
Prevention measures
Schools and parents can collaborate to reduce the spread of infectious diseases:
- Vaccinations: Following recommended vaccination schedules prevents avoidable diseases.
- Hygiene habits: Teaching and encouraging children to wash hands, cover coughs or sneezes, and not share personal items.
- Cleaning protocols: Regular cleaning of frequently touched surfaces and hygiene of shared equipment.
- Ventilation: Ensuring good air circulation in classrooms to reduce airborne pathogen concentration.
- Staying home when sick: Encouraging parents to follow the rule that children with symptoms of infectious diseases stay home.
Schools play an important role in preventing disease spread, and such preventive measures can significantly contribute to the health of the entire community.