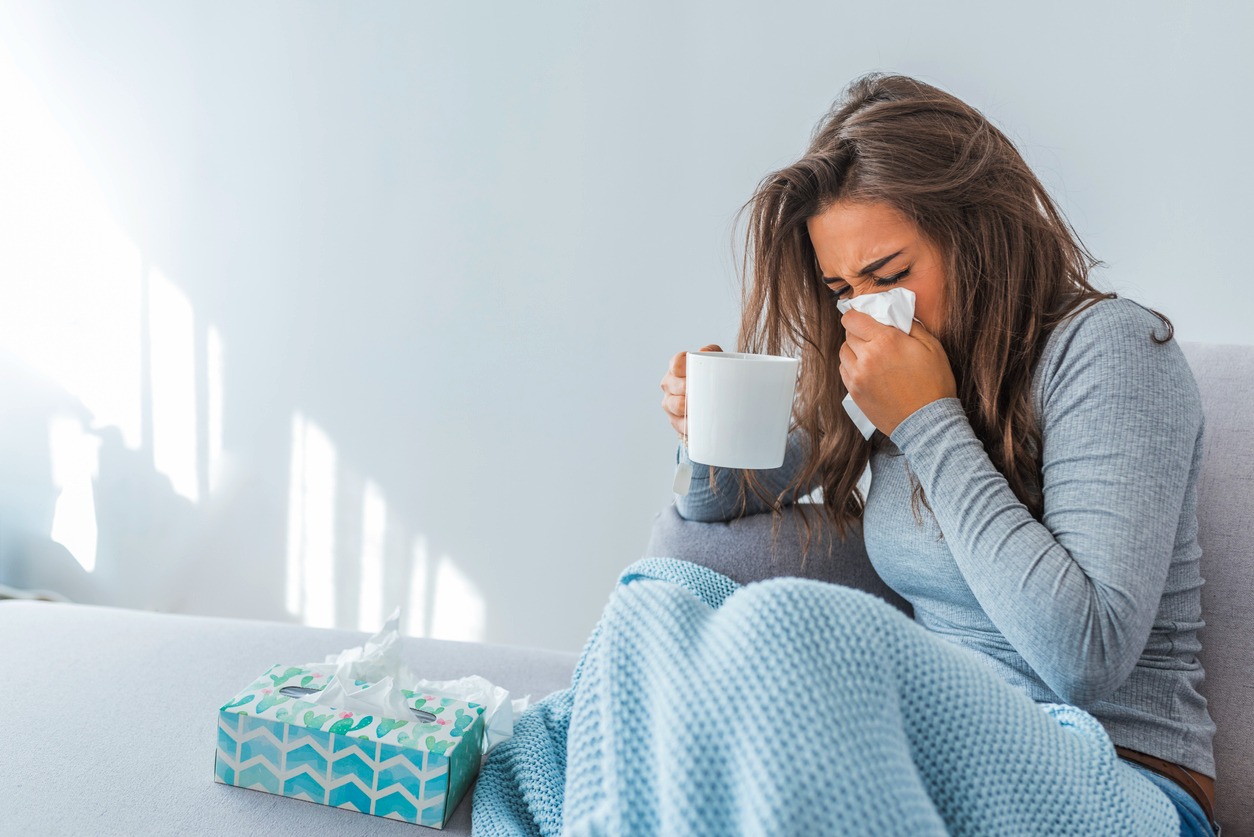
Flu is a viral infection that most commonly affects the respiratory tract – the nose, throat, and lungs. It spreads through airborne droplets or by direct contact with an infected person.
Types of flu:
Human influenza viruses are divided into three types: A, B, and C. Types A and B pose the greatest threat to public health as they are the main causes of epidemics.
Type A influenza virus has a wide host range: it can infect not only humans but also animals such as pigs, horses, marine mammals, and birds – both wild and domestic. Such broad virus circulation allows it to easily exchange genetic material, which is why type A influenza virus is responsible not only for epidemics but also for pandemics when the disease spreads worldwide.
Type C virus, on the other hand, causes only isolated mild illnesses and does not have significant public health importance.
Symptoms:
- High temperature (38°C or higher).
- Chills.
- Muscle and joint pain.
- Headache.
- Severe fatigue.
- Dry cough.
- Sore throat.
How does the flu spread?
- By coughing, sneezing, or talking (the virus enters the air).
- By touching surfaces or objects contaminated by an infected person.
Prevention:
1. Vaccination: Annual flu vaccines are the most effective way to protect against the flu.
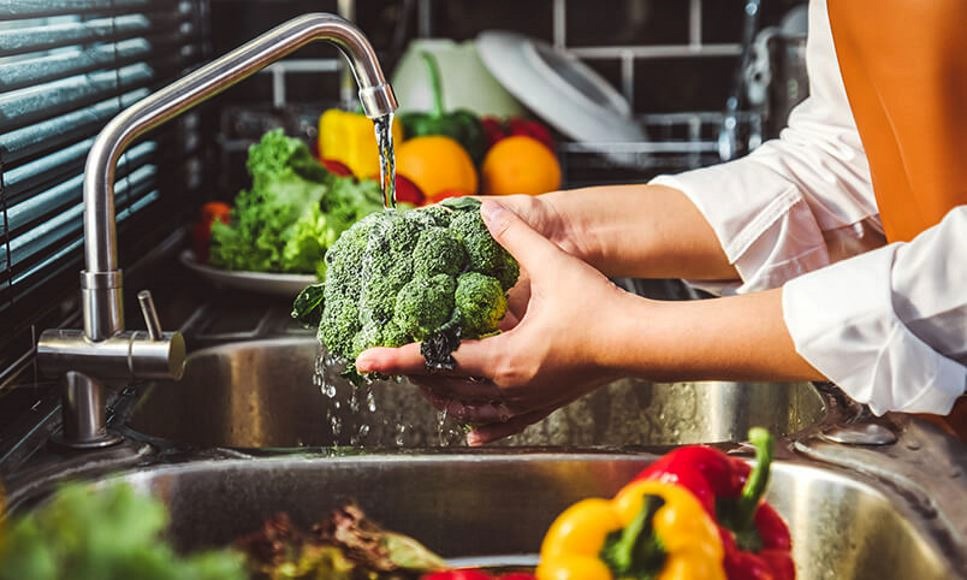
2. Hand hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water or use a disinfectant.
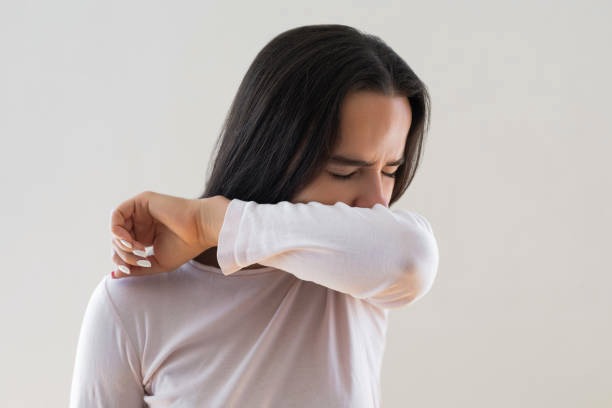
3. Cough etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with your elbow or a tissue when coughing or sneezing. Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth as much as possible.
4. Healthy lifestyle: Strengthen your immune system with proper nutrition, exercise, and adequate rest.
5. Reducing contacts: Avoid close contact with people who have the flu. Avoid crowded places.
Treatment:
- Rest: It is important to stay home and rest.
- Fluids: Drink plenty of warm beverages and fluids.
- Medications: Medicines can be used to reduce fever or relieve pain (e.g., paracetamol, ibuprofen).
- Antiviral drugs: If prescribed by a doctor, they can reduce the duration of symptoms.
When to see a doctor?
- If symptoms are very severe (e.g., breathing difficulties).
- If the flu becomes complicated (e.g., signs of pneumonia appear).
- If you have chronic diseases that may increase the risk of complications.
Although the flu often seems like a mild illness, it can cause very serious complications, and no one is completely protected from it. For this reason, it is important to take preventive measures and not forget vaccinations, which are the most effective way to protect against this unpleasant disease.
Take care of yourself and stay healthy ❤️
If you have any questions, contact us:
💌 Email: info@togilas.lt
📞 Mobile phone: 8 6 14 12278